|
|
The Caravan Case: Problem Statement
| Name |
The Caravan Case: Problem Statement |
| Description |
|
Given available data sources within MIC, and the
above defined direct marketing goals, the two
problems to solve can be defined as:
|
| |
|

|
- Given the total data set of 6000 customers, select a
subset with an increased response rate. The best way to do so is to simply
predict which customers will respond when approached. However, buying a caravan
policy will not be directly dependent of a simple combination of attributes in an
insurance company database. At best one hopes to find areas in the
database with increased chances for clients to be interested in caravan
policies are increased (and other areas with decreased chances). This implies
that at best one is able to predict the chance that a client is susceptible for
buying a policy. The problem to solve now becomes: predict the chance per
client of being interested in buying a caravan insurance company, and select
the subset with the highest chance (Classification).
The selection criterion to select the
subset has to be chosen in such a way that the ratio between the number of
responses and the costs (number of addressees in the campaign) is as high as
possible.
|
| |
|

|
- The main question that comes in mind when focussing on media that are attended by
prospective clients is: who are the clients of caravan policies, what
characterizes them? After all, if we can characterize them, we can infer
the media they will attend. In other words, in order to realise the second
goal the actual and potential customers of caravan policies have to be described
in terms of database attribute relationships. Simultaneously, one hopes
that this characterization is learnable, and makes clear why these customers buy a
caravan policy in such a way that the outcome is meaningful tot the marketeer.
(Characterization)
|
| |
|

|
In order to increase the response of the marketing campaign,
one has to find (classify) and
address through media (characterize)
these customers that could buy such a policy. In
other words, given that MIC data set, the target
function identifies and describes client groups
that resemble caravan policy owners, but
currently don’t have a policy.
|
| |
|

|
First, the prediction modelis
learned from the train records. These records
include the caravan policy ownership relation.
When satisfactory performance is
reached, the prediction model is used on the test
data to predict the chance on having a
caravan policy. The 800 clients with the highest
prediction are then selected for the
mailing.
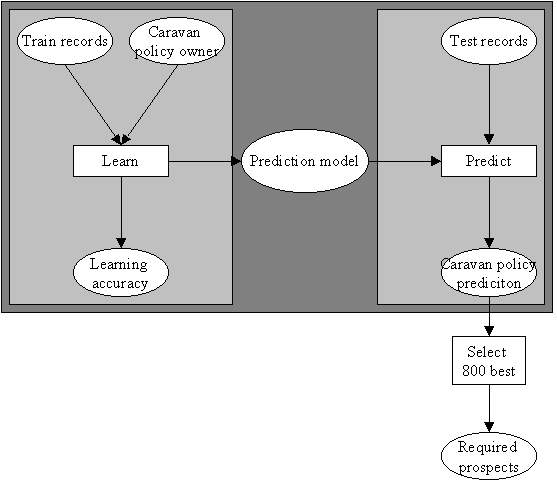
Figure 1 - General overview of the
classification process
|
| |
|
|
|
| Case Study |
The Caravan Policy Case
|
|
|

